李圣纯/张江团队系统总结了质体介导RNAi控虫领域研究进展
作者:九游会老哥俱乐部发布时间:2023年06月19日 14:13
近日,湖北大学李圣纯/张江团队受邀,在植物学经典权威期刊Plant Cell & Environment杂志上发表了题为“Plastid-mediated RNA interference: a potential strategy for efficient pest control”的综述文章。该文总结了质体介导RNAi(PM-RNAi)在控虫中的应用,PM-RNAi抗虫效率影响因素以及对未来该领域的发展做出了展望。九游会老哥俱乐部李圣纯副教授为论文的第一作者,张江教授为论文的通讯作者。该研究得到了国家自然科学基金等相关经费的支持。

图1 文章首页
RNAi是一种在真核生物中由双链RNA(dsRNA)诱发的基因沉默现象,截至目前,RNAi技术已经成为了一项新的抗虫技术,工作原理是设计与合成靶向害虫自身必需基因的dsRNA,通过害虫的摄取后诱发害虫体内的RNAi,从而抑制必需基因的表达降低害虫的适合度,甚至导致害虫死亡,最终达到抗虫的效果。由于质体(叶绿体)含有高拷贝数的基因组及RNA干扰(RNAi)通路的缺乏,可以使外源导入的dsRNA大量积累,可以显著提高对一些鞘翅目害虫如马铃薯甲虫和茄二十八星瓢虫的抗性。另外,西花蓟马特有的锉吸式口器能够摄入整个质体并获取其中的dsRNA或hpRNA,使得质体转化植株比核转化植物对西花蓟马有更高的致死率。类似的,PM-RNAi对能摄取质体内容物的桃蚜和叶螨都有明显的杀虫效果。然而,烟粉虱因无法摄取到质体中的dsRNA而对质体介导RNAi不敏感,而棉铃虫中肠存在高活性的dsRNA酶导致对PM-RNAi的不应性。
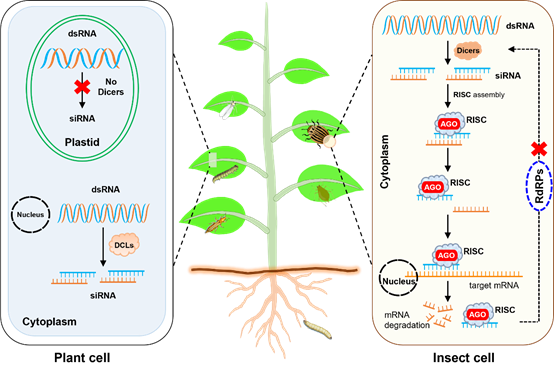
图2. 植物介导的RNAi技术控虫的模式图。
此文还总结影响PM-RNAi抗虫效率的其他因子:除了靶标序列的选择、昆虫肠道中的dsRNA酶活性、dsRNA的吸收与转运等因素,PM-RNAi的效率还受到其他因素的影响,包括质体中表达的dsRNA的长度、不同口器害虫的取食方式、非绿色组织中dsRNA的低表达量以及质体可转化物种的有限性等。针对以上问题,文中也提出了相应的解决方案。例如,利用T7表达系统进一步提高质体中的dsRNA含量,以及利用肠道微生物协同防控鞘翅目害虫;针对中肠中dsRNA酶活性较高的鳞翅目昆虫,提出了有效保护dsRNA以及在质体中生产的小干扰RNA和提高非绿色质体中的dsRNA表达量的解决方案。最后,本文就RNAi防控害虫的生物安全性,如RNAi抗性问题进行了讨论,为PM-RNAi在植物抗虫生物技术领域的发展提供了新的蓝图。
原文链接:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/pce.14652
相关文献:
1. Xu W, Zhang M, Li Y, et al. (2023) Complete protection from Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata by expressing long double-stranded RNAs in potato plastid. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology 65(4):1003–1011.
2. Wu M, Zhang Q, Dong Y, et al. (2023) Transplastomic tomatoes expressing double-stranded RNA against a conserved gene are efficiently protected from multiple spider mites. New Phytologist 237(4):1363–1373.
3. Dong Y, Wu M, Zhang Q, Fu J, Loiacono FV, Yang Y, Wang Z, Li S, Chang L, Bock R, Zhang J. (2022) Control of a sap-sucking insect pest by plastid-mediated RNA interference. Molecular Plant 15(7):1176-1191.
4. Fu J, Xu S, Lu H, et al. (2022) Resistance to RNA interference by plant-derived double-stranded RNAs but not plant-derived short interfering RNAs in Helicoverpa armigera. Plant, Cell & Environment 45(6):1930–1941.
5. Wu M, Dong Y, Zhang Q, et al. (2022) Efficient control of western flower thrips by plastid-mediated RNA interference. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 119: e2120081119.
6. Xu L, Xu S, Sun L, et al. (2021) Synergistic action of the gut microbiota in environmental RNA interference in a leaf beetle. Microbiome 9: 98.
7. He W, Xu W, Xu L, et al. (2020) Length-dependent accumulation of double-stranded RNAs in plastids affects RNA interference efficiency in the Colorado potato beetle. Journal of Experimental Botany 71: 2670–2677.
8. Zhang J, Khan SA, Hasse C, et al. (2015) Pest control. Full crop protection from an insect pest by expression of long double-stranded RNAs in plastids. Science 347:991–994.



